The latest benchmarks of Intel’s next-generation Ice Lake-SP Xeon CPU server family have leaked out and they show some interesting results when compared to AMD’s current generation 3rd Gen EPYC Rome CPUs.
Intel’s Next-Gen 10nm Ice Lake-SP CPUs Tested, Two Chips With 28 Cores and 56 Threads Each Against A Single AMD EPYC Rome 64 Core Flagship
As part of the Whitley platform, the Intel Ice Lake-SP CPU lineup will be composed of several Xeon chips. We have already seen 6 core and 24 core parts but the latest one is a 28 core part and has been spotted by TUM_APISAK in the Geekbench database and Momomo_US too in the SiSoftware database.
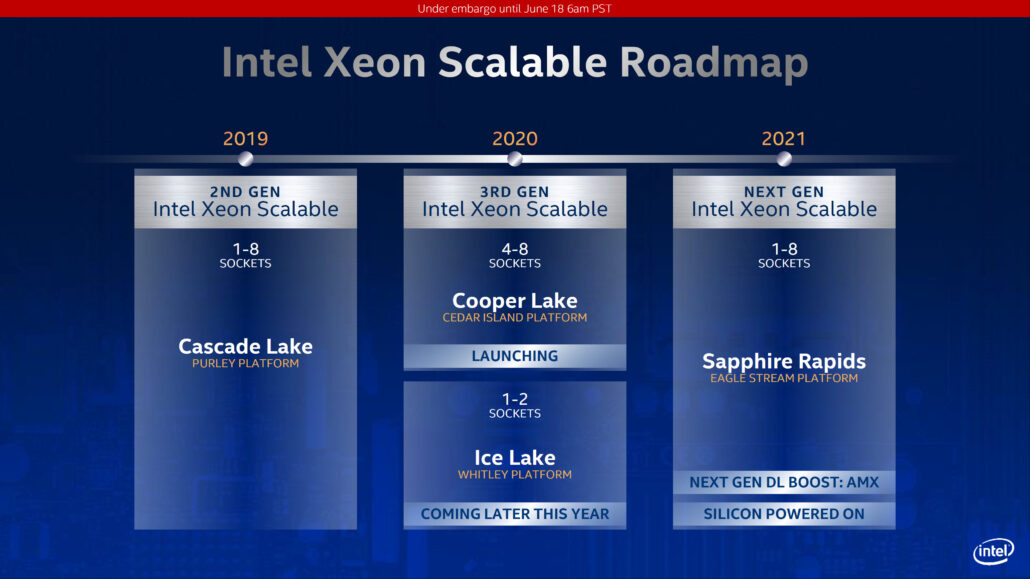
The Intel Ice Lake-SP CPU was tested on a dual-socket server and features two of the chips. Each chip features 28 cores and 56 threads which round up to 56 cores and 112 threads in total. Since the chip is still an early engineering sample, it features lower clock speeds of 1.5 GHz base and up to 3.20 GHz boost clocks. The CPU features 42 MB of L3 and 35 MB of L2 cache for a total of 77 MB cache. The 2S Ice Lake-SP server was equipped with 512 GB of memory which should be clocked at 3200 MHz and featured in an 8-channel configuration which is one of the key highlights of the new Whitley platform.
The performance of the 2S Intel Ice Lake-SP server was evaluated within Geekbench 4 which does benefit from the AVX-512 instruction set featured on Intel’s current & upcoming Xeon CPU families. In single-core tests, the server scored up to 3443 points and in multi-core tests, the chip scored up to 37317 points.
Before we compare it to the AMD EPYC 7742, it should be pointed that both of these test results are based on early engineering samples with lower clock speeds so final performance is expected to be much better. However, at the same time, the Intel CPUs benefit in this benchmark from their AVX-512 instruction set which the AMD CPUs lack. The entries are also shown in different operating system environments though the EPYC 7742 CPU was in fact tested on a Windows 10 server setup, Geekbench isn’t reporting it correctly. Regardless of that, let’s see how the two 28 core Ice Lake-SP Xeon CPUs stack against a single AMD EPYC 7742 CPU.
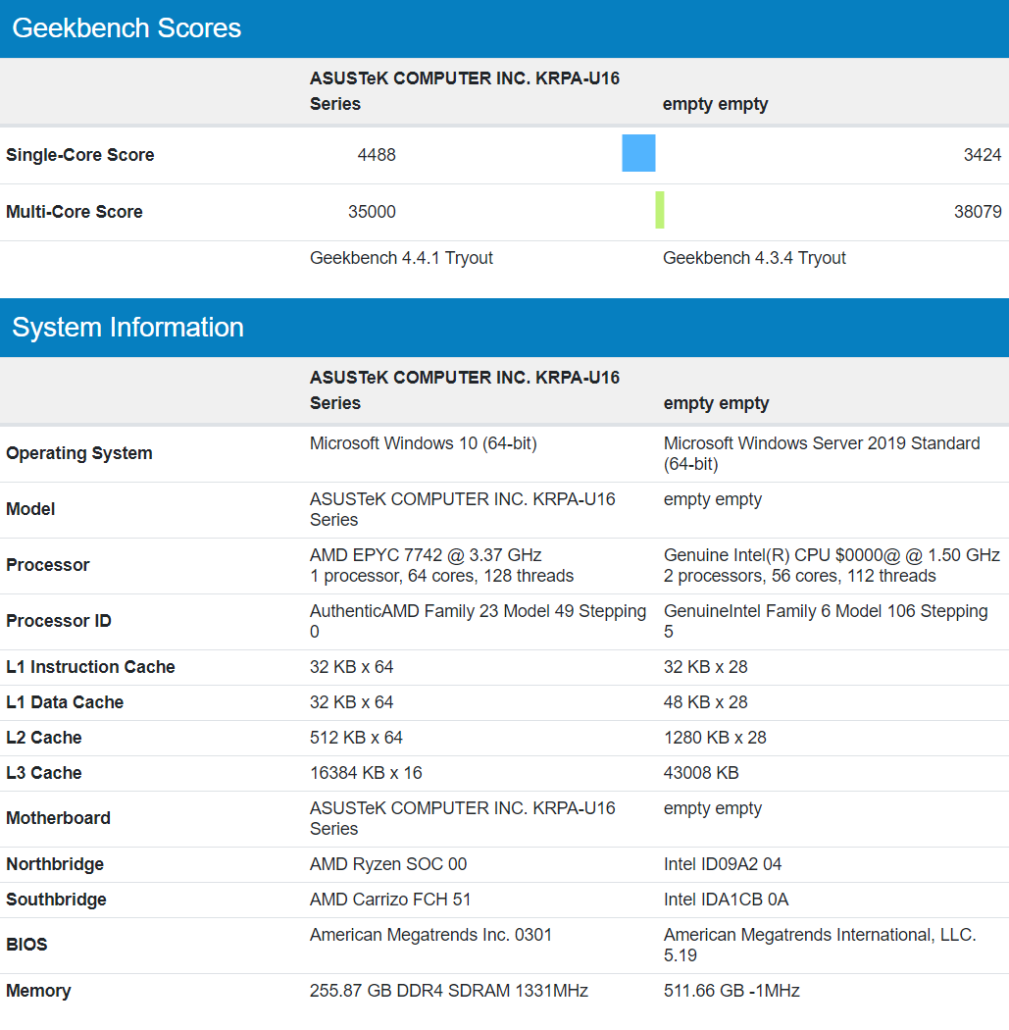
We used a single EPYC 7742 entry for comparison so we are comparing a total of 64 cores and 128 threads from AMD against 56 cores and 112 threads from Intel. The AMD EPYC 7742 CPU easily out performs the Intel chips in single-core tests which is due to the higher base clock speeds of 3.4 GHz versus 1.5 GHz on the Intel parts. At the same time, the AMD platform delivers around 35000 multi-core points which are slightly lower than the Intel Ice Lake-SP parts. With final clock speeds, the Ice Lake-SP CPUs can easily outperform the AMD EPYC Rome parts but the lead may not be as big as Intel had hoped for.
It obviously looks like Intel’s Ice Lake-SP was more of an EPYC Rome competitor which missed its initial schedule due to poor 10nm yields and now has to compete against AMD’s EPYC Milan that is just around the corner. We will wait to see some more test and performance results for Ice Lake-SP CPUs in non-AVX 512 optimized workloads but every benchmark leak makes it very clear that Ice Lake-SP is late and AMD isn’t going to make things any better for Intel.
And it also just isn’t about the performance metrics, we still don’t know the prices and power efficiency of Ice Lake-SP yet but we do know that the existing EPYC Rome lineup has far lower prices and TCO than the Cascade Lake-SP lineup and that is expected to remain intact even when Ice Lake-SP ships.
Intel Xeon SP Families:
| Family Branding | Skylake-SP | Cascade Lake-SP/AP | Cooper Lake-SP | Ice Lake-SP | Sapphire Rapids | Granite Rapids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process Node | 14nm+ | 14nm++ | 14nm++ | 10nm+ | 10nm++ | 7nm+? |
| Platform Name | Intel Purley | Intel Purley | Intel Cedar Island | Intel Whitley | Intel Eagle Stream | Intel Eagle Stream |
| MCP (Multi-Chip Package) SKUs | No | Yes | No | Yes | TBD | TBD |
| Socket | LGA 3647 | LGA 3647 BGA 5903 |
LGA 4189 | LGA 4189 | LGA 4677 | LGA 4677 |
| Max Core Count | Up To 28 | Up To 28 Up To 48 |
Up To 28 | TBD | TBD | TBD |
| Max Thread Count | Up To 56 | Up To 56 Up To 96 |
Up To 56 | TBD | TBD | TBD |
| Max L3 Cache | 38.5 MB L3 | 38.5 MB L3 66 MB L3 |
38.5 MB L3 | TBA (1.5 MB Per Core) | TBD | TBD |
| Memory Support | DDR4-2666 6-Channel | DDR4-2933 6-Channel DDR4 2933 12-Channel |
Up To 6-Channel DDR4-3200 | Up To 8-Channel DDR4-3200 | 8-Channel DDR5 | 8-Channel DDR5 |
| PCIe Gen Support | PCIe 3.0 (48 Lanes) | PCIe 3.0 (48 Lanes) | PCIe 3.0 (48 Lanes) | PCIe 4.0 (64 Lanes) | PCIe 5.0 | PCIe 5.0 |
| TDP Range | 140W-205W | 165W-205W | 150W-250W | ~250W-~300W | TBD | TBD |
| 3D Xpoint Optane DIMM | N/A | Apache Pass | Barlow Pass | Barlow Pass | Crow Pass | Donahue Pass |
| Competition | AMD EPYC Naples 14nm | AMD EPYC Rome 7nm | AMD EPYC Rome 7nm | AMD EPYC Milan 7nm+ | AMD EPYC Genoa ~5nm | AMD Next-Gen EPYC (Post Genoa) |
| Launch | 2017 | 2018 | 2020 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022-2023? |
Intel Xeon 10nm+ Ice Lake-SP Family
Intel Ice Lake-SP processors will be shipping later this year and will be based on the 10nm+ process node. We have seen earlier slides say that the Ice Lake family would feature up to 28 cores but the one from ASUS’s presentation says that it would actually feature up to 38 cores & 76 threads per socket. There are also rumors indicating up to 56 cores and 112 threads so we cannot say for sure what will the actual core counts on the new chips look like.
The main highlight of Ice Lake-SP processors will be support for PCIe Gen 4 and 8-channel DDR4 memory. The Ice Lake Xeon family would offer up to 64 PCIe Gen 4 lanes and would offer support for 8-channel DDR4 memory clocked at 3200 MHz (16 DIMM per socket with 2nd Gen Persistent memory support). Intel Ice Lake Xeon processors would be based on the brand new Sunny Cove core architecture which delivers an 18% IPC improvement versus the Skylake core architecture that has been around since 2015.

One thing to note is that Intel’s 10nm for 2020 is an enhanced node of the original 10nm node that will mark its debut with the Tiger Lake CPUs. It’s marked as 10nm+ and that is specifically what the Ice Lake-SP Xeon line will make use of. Some of the major upgrades that 10nm will deliver include:
- 2.7x density scaling vs 14nm
- Self-aligned Quad-Patterning
- Contact Over Active Gate
- Cobalt Interconnect (M0, M1)
- 1st Gen Foveros 3D Stacking
- 2nd Gen EMIB
The Intel Ice Lake-SP lineup would be directly competing against AMD’s enhanced 7nm based EPYC Milan lineup which will feature the brand new 7nm Zen 3 core architecture which is confirmed to be one of AMD’s biggest architectural upgrade since the original Zen core. Expect to see more Intel & NVIDIA based servers in the coming months.







More Stories
AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT “Big Navi” GPU Alleged 3DMark Benchmarks Leaked – Faster Than GeForce RTX 3080 at 4K, Slower In Port Royal Ray Tracing
AMD Ryzen 7 5800H 8 Core & 16 Thread Cezanne ‘Zen 3’ High-Performance CPU Shows Up, Early ES Chip With 3.2 GHz Clocks
BitFenix Announces Two New Cases, The Nova Mesh SE and the Nova Mesh SE TG